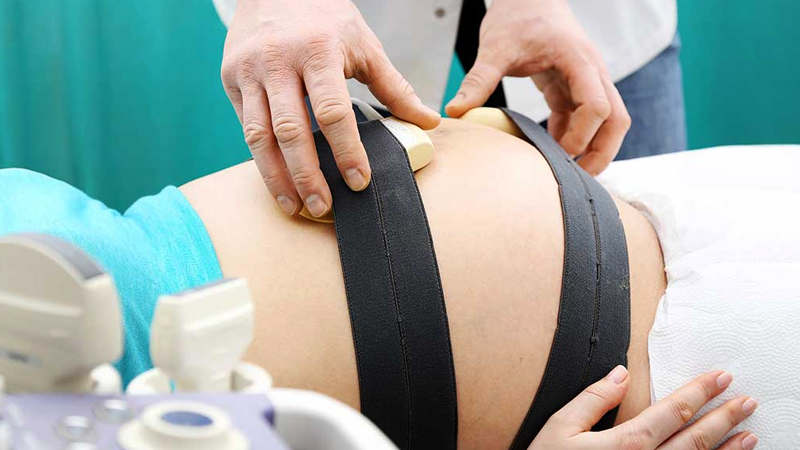
CTG / NST Machine
A Cardiotocography (CTG) and a Non-Stress Test (NST) are both forms of fetal monitoring used during pregnancy to assess the well-being of the fetus. These tests are typically conducted in the later stages of pregnancy, particularly if there are concerns about fetal health or if the pregnancy is considered high-risk.
Cardiotocography (CTG)
A Cardiotocography, often referred to as a CTG or fetal monitoring, is a procedure that simultaneously records the fetal heart rate (FHR) and uterine contractions. It is commonly used during labor to monitor the baby's heart rate and the strength and duration of contractions.
Components:
- Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) Monitor: Detects and records the baby's heart rate. This can be done externally using ultrasound transducers placed on the mother's abdomen, or internally using a scalp electrode attached to the baby's scalp.
- Uterine Contraction Monitor: Records the frequency, duration, and intensity of uterine contractions. This is typically achieved using a pressure-sensitive device placed on the mother's abdomen.
Interpretation:
- Baseline Fetal Heart Rate: The average heart rate over a 10-minute period. Normal range is typically between 110-160 beats per minute.
- Variability: Fluctuations in the heart rate. Absence of variability can indicate fetal distress.
- Accelerations and Decelerations: Changes in the heart rate pattern. Accelerations are generally a reassuring sign, while decelerations may indicate fetal compromise.
- Contractions: Frequency, duration, and intensity are monitored to assess uterine activity.
Non-Stress Test (NST)
A Non-Stress Test is a simple, non-invasive test that measures the baby's heart rate in response to its own movements. It is usually performed in the third trimester of pregnancy to assess fetal well-being.
Procedure:
- The mother reclines in a comfortable position, and sensors are placed on her abdomen to monitor the baby's heart rate.
- The baby's movements are observed, and the fetal heart rate is recorded.
- The test typically lasts for about 20-30 minutes but can be extended if necessary to gather sufficient data.
Interpretation:
- Reactive NST: A reassuring result where the baby's heart rate increases (accelerates) in response to movement.
- Non-Reactive NST: If the baby's heart rate does not accelerate appropriately with movement, further evaluation may be required to assess fetal well-being.
Differences:
- Purpose: CTG monitors both fetal heart rate and uterine contractions during labor, while NST focuses solely on fetal heart rate response to movement.
- Timing: CTG is often used during labor, while NST is typically performed in the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Duration: CTG monitoring can be continuous throughout labor, while NST is usually a shorter, intermittent test.
Both CTG and NST are valuable tools in assessing fetal well-being and guiding clinical management decisions during pregnancy. The choice of test depends on the specific clinical circumstances and the stage of pregnancy.
