Diagnostic Hysterolaparoscopy
Diagnostic hysterolaparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that combines hysteroscopy and laparoscopy to diagnose and evaluate conditions within the female reproductive system. This procedure allows direct visualization of both the uterine cavity and the pelvic organs, providing comprehensive information for diagnosing various gynecological conditions.
Indications
Diagnostic hysterolaparoscopy is indicated for:
- Infertility Evaluation: To investigate potential causes of infertility.
- Pelvic Pain: To identify sources of chronic pelvic pain.
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: To diagnose causes of irregular or heavy bleeding.
- Endometriosis: To detect and assess the extent of endometriosis.
- Fibroids: To evaluate the presence and impact of uterine fibroids.
- Adhesions: To identify scar tissue that may cause pain or fertility issues.
- Congenital Uterine Anomalies: To examine structural abnormalities of the uterus.
Procedure
The procedure involves two main parts: hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
Hysteroscopy
- Anesthesia: Local, regional, or general anesthesia is administered.
- Insertion: A hysteroscope (a thin, lighted tube) is inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterine cavity.
- Inspection: The uterine cavity is filled with a saline solution to expand it, allowing for clear visualization of the uterine lining, endometrial polyps, fibroids, and other abnormalities.
- Documentation: Images and videos are often taken for documentation and further analysis.
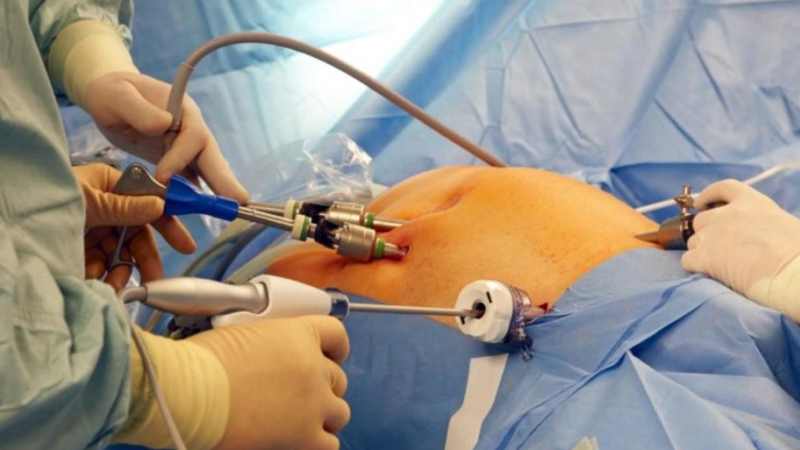
Laparoscopy
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is usually administered.
- Incisions: Small incisions (usually 3-4) are made in the abdomen, typically around the navel and lower abdomen.
- Laparoscope Insertion: A laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) is inserted through one of the incisions, providing a view of the pelvic organs on a video screen.
- Inspection: The pelvic organs, including the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and surrounding tissues, are examined for abnormalities such as endometriosis, adhesions, cysts, or tumors.
- Documentation: Images and videos are taken for further evaluation.
Recovery
- Hospital Stay: Usually performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to go home the same day.
- Postoperative Care: Patients are monitored in a recovery area until the effects of anesthesia wear off.
- Activity: Light activities can be resumed within a few days, but strenuous activities and heavy lifting should be avoided for about 1-2 weeks.
- Follow-up: A follow-up appointment with the healthcare provider is scheduled to discuss the findings and plan further treatment if needed.
Benefits
- Comprehensive Diagnosis: Allows simultaneous evaluation of the uterine cavity and pelvic organs.
- Minimally Invasive: Small incisions result in less pain, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery compared to open surgery.
- Direct Visualization: Provides direct visualization of abnormalities that might not be detected through imaging studies alone.
Risks and Complications
- Bleeding: Some bleeding may occur during or after the procedure.
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the incision sites or within the pelvic cavity.
- Organ Injury: There is a small risk of injury to the uterus, bladder, bowel, or blood vessels.
- Anesthesia Risks: As with any procedure involving anesthesia, there are risks related to the use of anesthetic agents.
Alternatives
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans can provide detailed images of the pelvic organs, though they do not offer the direct visualization that hysterolaparoscopy does.
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy Alone: For cases where uterine cavity examination is not needed, diagnostic laparoscopy may be sufficient.
- Hysteroscopy Alone: For issues confined to the uterine cavity, hysteroscopy alone may be adequate.
Patients should discuss their specific symptoms, medical history, and diagnostic needs with their healthcare provider to determine if diagnostic hysterolaparoscopy is the appropriate choice for them.
