Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex endocrine disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It is characterized by various symptoms and has potential long-term health implications. Here's a comprehensive overview:
Symptoms
Menstrual Irregularities
- Infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual cycles.
- Absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) or heavy periods.
Hyperandrogenism
- Elevated levels of male hormones (androgens).
- Symptoms include excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), severe acne, and male-pattern baldness.
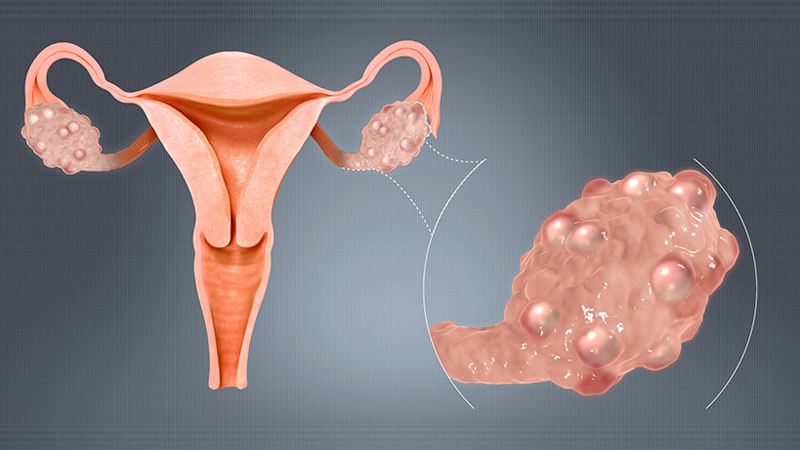
Polycystic Ovaries
- Enlarged ovaries containing numerous small cysts visible via ultrasound.
Weight Gain
- Many women with PCOS experience weight gain or have difficulty losing weight.
Insulin Resistance
- A significant number of women with PCOS have insulin resistance, which can lead to type 2 diabetes.
Infertility
- PCOS is a leading cause of infertility due to ovulatory dysfunction.
Causes
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute:
- Genetic Factors: PCOS tends to run in families, indicating a genetic component.
- Insulin Resistance: High insulin levels can increase androgen production, affecting ovarian function.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Elevated levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and reduced levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG).
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation is common in women with PCOS and may contribute to increased androgen levels.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History: Assessing menstrual irregularities and symptoms of hyperandrogenism.
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs such as excess hair growth, acne, and obesity.
- Blood Tests: Measuring hormone levels, including androgens, LH, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and insulin.
- Ultrasound: Imaging of the ovaries to check for the presence of cysts.
Treatment
While there is no cure for PCOS, treatments focus on managing symptoms and preventing complications:
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss through diet and exercise can significantly reduce symptoms.
- Medications:
- Hormonal Birth Control: To regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels.
- Anti-Androgens: To reduce symptoms of hyperandrogenism.
- Metformin: Used to treat insulin resistance.
- Fertility Medications: For women trying to conceive, such as clomiphene citrate or letrozole.
- Cosmetic Treatments: For hirsutism, such as laser hair removal or electrolysis.
Complications
PCOS can lead to several long-term health issues:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Endometrial Cancer: Due to prolonged exposure to unopposed estrogen.
- Sleep Apnea
- Depression and Anxiety
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage PCOS symptoms:
- Balanced Diet: Low in refined carbohydrates to help manage insulin levels.
- Regular Exercise: Helps with weight control and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga or meditation can reduce stress, which may help balance hormones.
